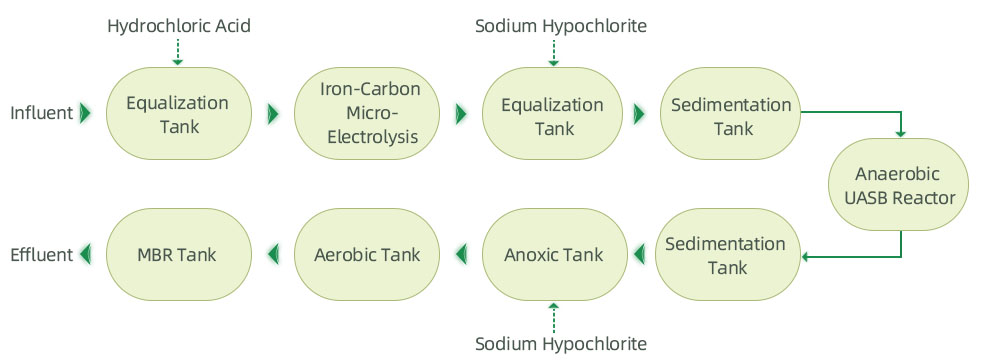
1.1.Key Pollutants:
2,3-Dichloropyridine, Oxadiazon API, D-threo-p-methylsulfonylphenylserine ethyl ester, 2,5-Diamino-4,6-dihydroxypyrimidine hydrochloride, and (1R,4S)-1-Amino-4-hydroxymethyl-2-cyclopentene hydrochloride, among other pharmaceutical intermediates and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
1.2 Key Characteristics:
① High salinity
② High organic nitrogen content
③ High total nitrogen
④ High ammonia nitrogen
⑤ Complex influent composition
⑥ Shock loads