1.High mineral content (hard water)
2.High alkalinity
3.Complex COD composition
4.High Kjeldahl nitrogen
Solution:MicroMotion®-N were applied to improve sludge activity and rapidly establish a stable nitrification system. The project met its retrofit objectives, with tailored upgrade plans, training materials, and experimental protocols provided based on on-site requirements.
Processing Scale:130m³/h
Treatment Effect:The treatment capacity of Corridor 1-6-7 reached ≥50 m³/h, with effluent ammonia nitrogen stably maintained at ≤25 mg/L.
 Characteristics
Characteristics
1.High mineral content (hard water)
2.High alkalinity
3.Complex COD composition
4.High Kjeldahl nitrogen
 Plant Profile
Plant Profile
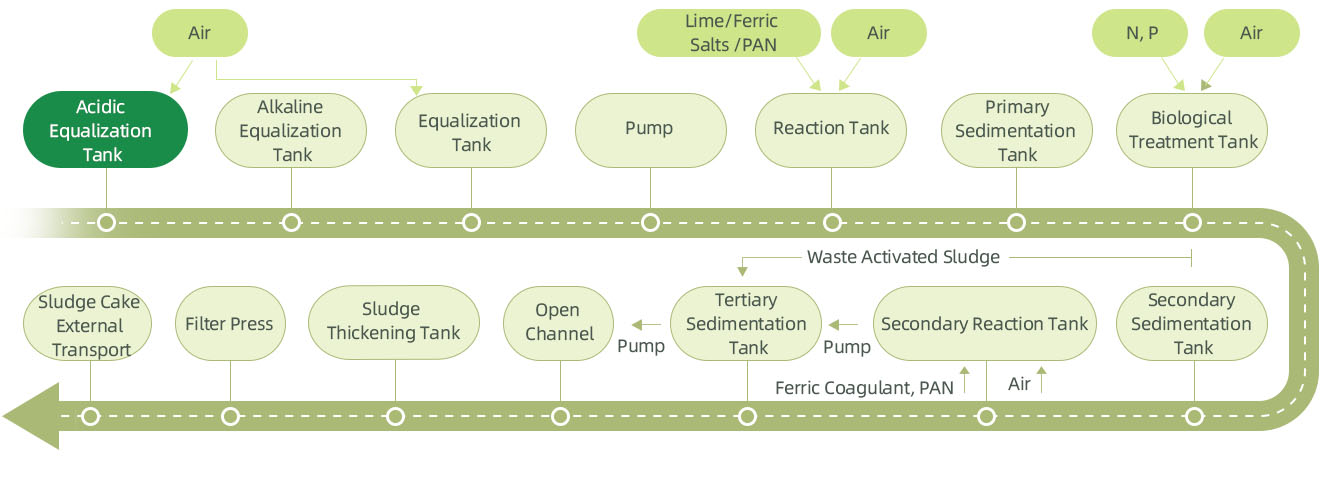
 Description
Description
System influent COD: 500–600 mg/L,
System influent ammonia nitrogen (NH₃-N): 250 mg/L,
System influe pH: 7.5–8.5.
Although all indicators initially met discharge standards during early operation, the system was later affected by influent ammonia nitrogen, hardness, and suspended solids (SS). As a result, the treatment capacity of a single corridor was approximately 15 m³/h, which fell short of the design requirement.
 Option
Option
(1) Activated Sludge Dosing: Added a total of 45 tons of biological sludge (with 80% moisture content) on September 20, 22, and 30, with 15 tons dosed each time.
(2) Acclimation and Cultivation: Started the sludge acclimation and biofilm formation stage in October. During this period, the flow rate was gradually increased from 5 m³/h to 15 m³/h, with dissolved oxygen maintained at approximately 4 mg/L. Following recommendations, crude methanol (98%) and disodium hydrogen phosphate were added to the O-tank inlet as carbon and phosphorus sources.
(3) Bacterial Inoculation: Applied MicroMotion®-N to the biological wastewater treatment system to improve sludge activity and rapidly establish a stable nitrification process.
 Result
Result
After inoculation with MicroMotion®-N, effluent ammonia nitrogen significantly decreased within 2–5 days; by days 5–20, ammonia nitrogen levels were maintained at ≤ 40 mg/L.
After commissioning:
The 1-6-7 corridor achieved a treatment capacity of ≥ 50 m³/h.
Effluent ammonia nitrogen remained stable at ≤ 25 mg/L.
 Periodic Service
Periodic Service
